How to Use Endoscopy for Gastrointestinal Surgeries in Exotic Pets?
- Share
- Issue Time
- Jul 29,2024
Summary
Endoscopy is a powerful and versatile tool for diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal issues in exotic pets.
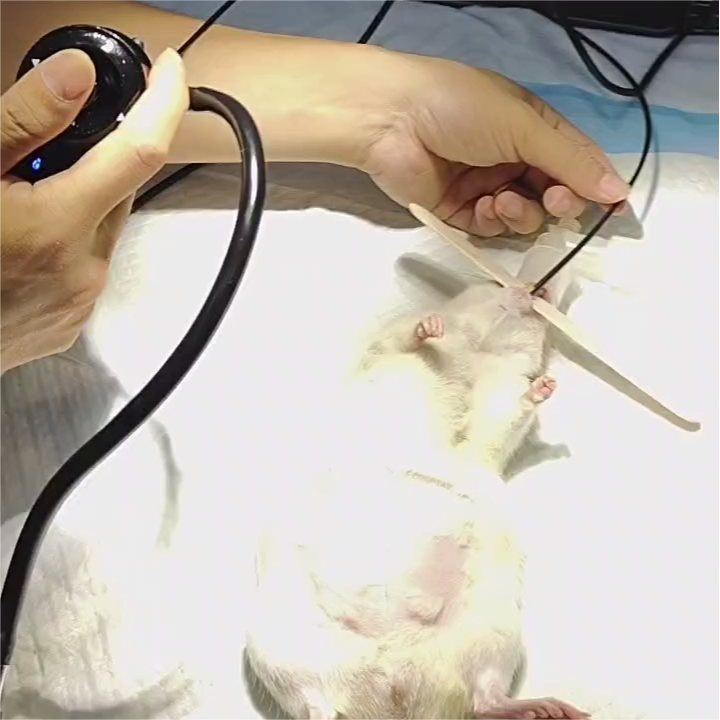
Endoscopy has become an invaluable tool in veterinary medicine, particularly for diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal issues in exotic pets. These minimally invasive procedures offer significant advantages over traditional surgical methods, including reduced recovery times and less stress for the animals. This blog will provide a comprehensive guide on how to perform gastrointestinal endoscopy on exotic pets, highlighting the necessary equipment, procedural steps, and key considerations to ensure successful outcomes.
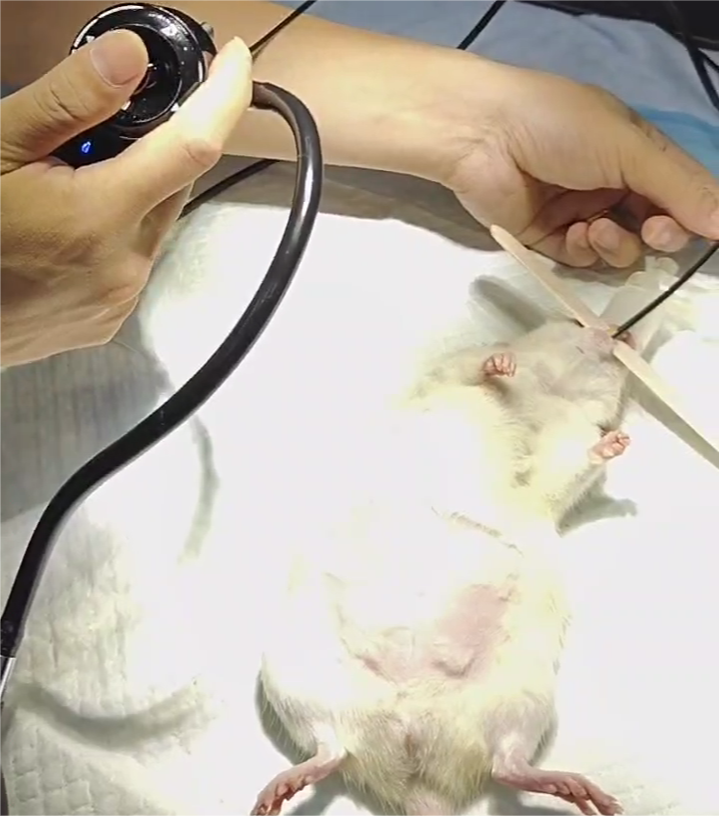
Guidelines for Endoscopic Gastrointestinal Surgery in Exotic Pets
Essential Equipment
Performing endoscopy on exotic pets requires specialized equipment designed to accommodate their unique anatomical structures. The following is a list of essential tools:
Flexible Endoscope: Choose a high-resolution, flexible endoscope with a small diameter suitable for the size of the exotic pet.
Insufflator: To gently distend the gastrointestinal tract for better visualization.
Biopsy Forceps: For taking tissue samples if needed.
Foreign Body Retrieval Tools: Such as grasping forceps or snares for removing ingested objects.
Anesthesia Equipment: To safely anesthetize the pet during the procedure.
Preoperative Preparation
Before performing the endoscopic procedure, thorough preoperative preparation is crucial:
Patient Evaluation: Conduct a complete physical examination and review the pet’s medical history. Blood tests and imaging studies (e.g., radiographs or ultrasound) may be necessary to assess the condition.
Fasting: Ensure the pet has fasted appropriately to minimize the risk of regurgitation and improve visibility during the procedure.
Anesthesia Protocol: Develop an anesthesia plan tailored to the species and health status of the exotic pet. Continuous monitoring of vital signs is essential throughout the procedure.
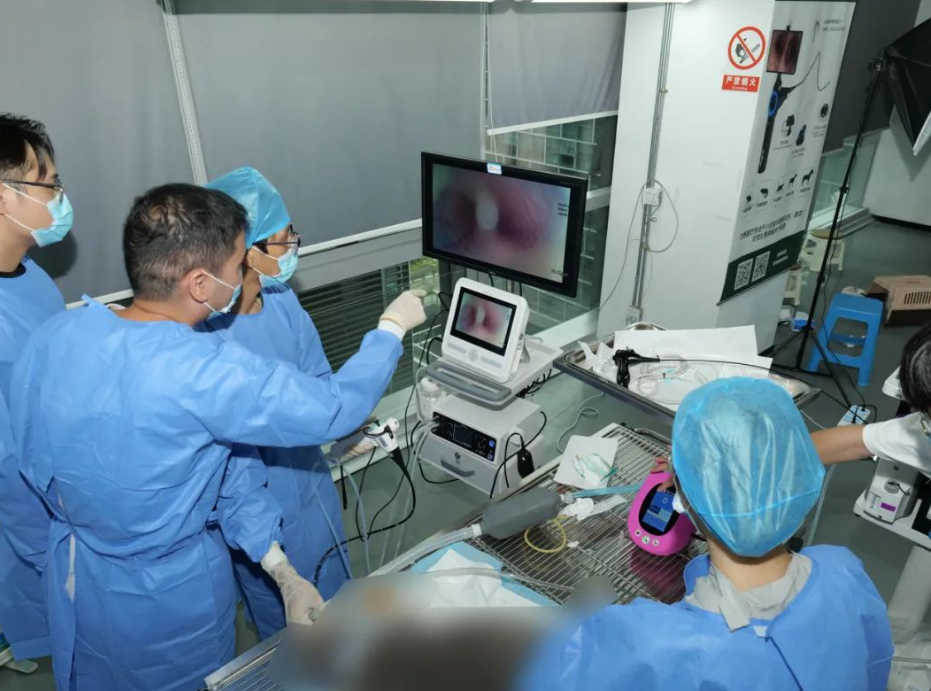
Procedural Steps
Anesthesia and Positioning: Induce anesthesia and position the pet appropriately, usually in lateral or dorsal recumbency, depending on the species and the area of interest.
Insertion of the Endoscope: Gently insert the lubricated endoscope into the pet’s oral cavity, advancing it slowly through the esophagus into the stomach and intestines.
Visualization and Examination: Use the endoscope to thoroughly examine the gastrointestinal tract, looking for abnormalities such as ulcers, tumors, or foreign bodies.
Biopsy or Foreign Body Removal: If necessary, use the biopsy forceps to obtain tissue samples for histopathological examination. For foreign body removal, carefully maneuver the retrieval tool to grasp and extract the object.
Completion and Recovery: Once the examination or intervention is complete, slowly withdraw the endoscope. Monitor the pet during the recovery phase from anesthesia.
Postoperative Care
After the endoscopic procedure, proper postoperative care is vital for the pet’s recovery:
Monitoring: Observe the pet closely for any signs of complications, such as vomiting, lethargy, or abdominal pain.
Medication: Administer any prescribed medications, such as analgesics or antibiotics, as directed by the veterinarian.
Feeding: Gradually reintroduce food based on the pet’s tolerance and recovery progress. Soft or liquid diets may be recommended initially.
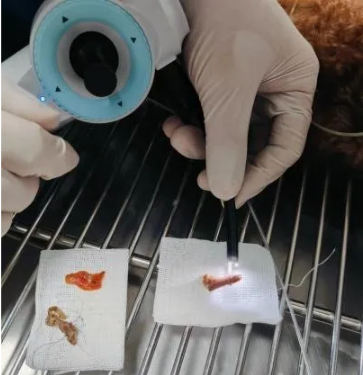
Key Considerations
Species-Specific Variations: Understand the anatomical and physiological differences among various exotic pet species to tailor the procedure accordingly.
Training and Experience: Proficiency in endoscopic techniques requires specialized training and practice. Consider seeking mentorship or attending workshops to enhance your skills.
Equipment Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain endoscopic equipment to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Endoscopy is a powerful and versatile tool for diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal issues in exotic pets. By proper procedural protocols and considering the unique needs of each species, veterinarians can achieve successful outcomes with minimal invasiveness. Continuous education and hands-on experience are key to mastering this advanced technique and providing the highest standard of care for exotic pet patients.
JeetVet is a veterinary endoscope manufacturer that provides endoscopy equipment solutions for exotic animals. Click to learn more information.